
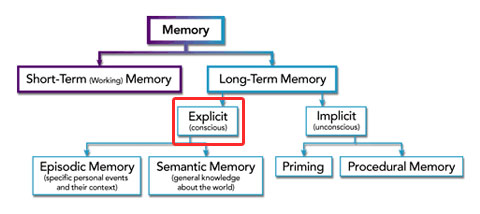
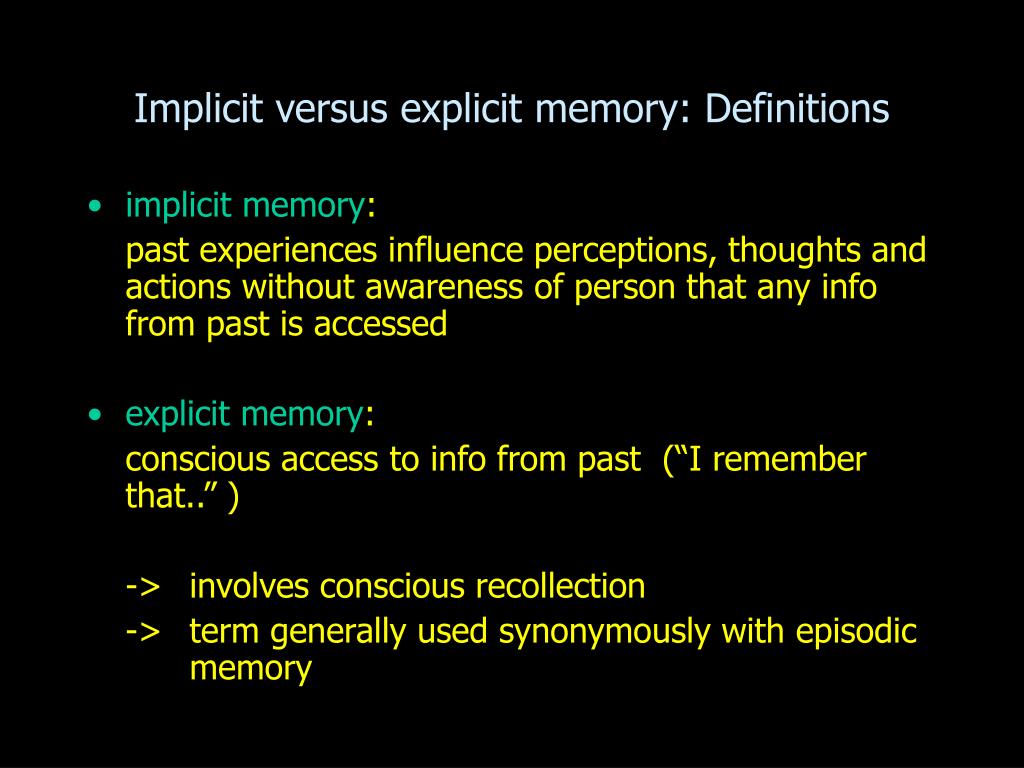
They can be divided into those that involve recalling personal experiences and those that involve remembering facts and information. Riding a bike relies on implicit memory Explicit MemoryĮxplicit memory refers to conscious memories that we can intentionally recall and articulate. Eventually, the dogs learned to associate the bell with food. In this example, a neutral stimulus (a bell) was paired with a meaningful stimulus (food). Classical conditioning is the so-called ‘Pavlov’s Dog’ response, in which the individual learns by association.These effects are often subtle and can be used to manipulate the behavior of individuals! Priming is a complex psychological phenomenon where the exposure to one stimulus (such as a word, image, or action) affects how an individual will respond to a second stimulus.They are often associated with ‘muscle memory’ or specific actions being second nature.
#Explicit memory how to#
Procedural memories include how to drive a car, knit, play an instrument, or play a video game.Intentional memories influence our current behavior without us intentionally retrieving those memories. They are often tricky to articulate and explain and are usually more emotional and perceptional. Implicit memory refers to unconscious memories. Explicit and implicit memory systems involve distinct, but related, processes Implicit Memory Despite their clear distinction, evidence suggests that implicit memory can influence explicit memory. These two systems reflect different states of awareness and involve distinct neural processes. Long-term memory can be classified into two fundamental types: implicit and explicit memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
